Explain Metabolism of Different Organic Compound
Synthesis of all these relies on a single. Define the term metabolism Metabolism reactions in which organic compounds are from BCH 451 at North Carolina State University.
Ch105 Chapter 6 A Brief History Of Natural Products And Organic Chemistry Chemistry
Organic Compounds Definition Organic compounds are a type chemical compounds where one or more than one carbon covalently bonded with each other and with other atom like.

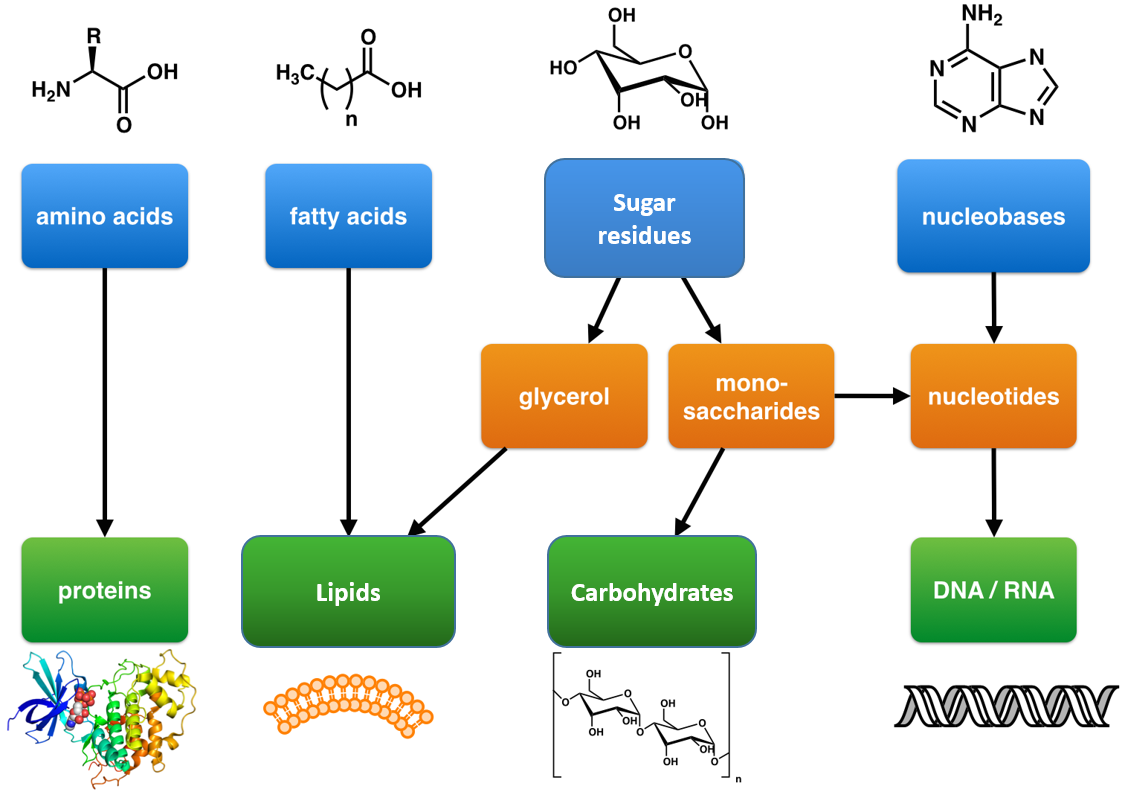
. These include nucleic acids fats sugars proteins enzymes and. Photoheterotrophs produce ATP through photophosphorylation but use environmentally obtained organic compounds to build. Organic compounds are those that have carbon atoms.
The most important is its ability to form long chains of. Think of thorns irritants and secondary metabolites. Plants cannot run or hide from their predators and have evolved many strategies to deter those who would eat them.
Metabolism Educational Goals 1. Flowchart summarizing the. Types of microbial metabolism.
Also within the scope of bacterial metabolism is the study of the uptake and utilization of the inorganic or organic compounds required for growth and maintenance of a cellular steady. Chapter 15 Lecture Notes. Examples of Organic Compounds or Molecules Molecules associated with living organisms are organic.
These molecules consist of carbon hydrogen and oxygen in a ratio of roughly 121. There are two mechanisms of ATP synthesis. Metabolism Sum of all the chemical reactions that take place in every cell of a living organism providing energy for the processes of life and synthesizing new cellular material.
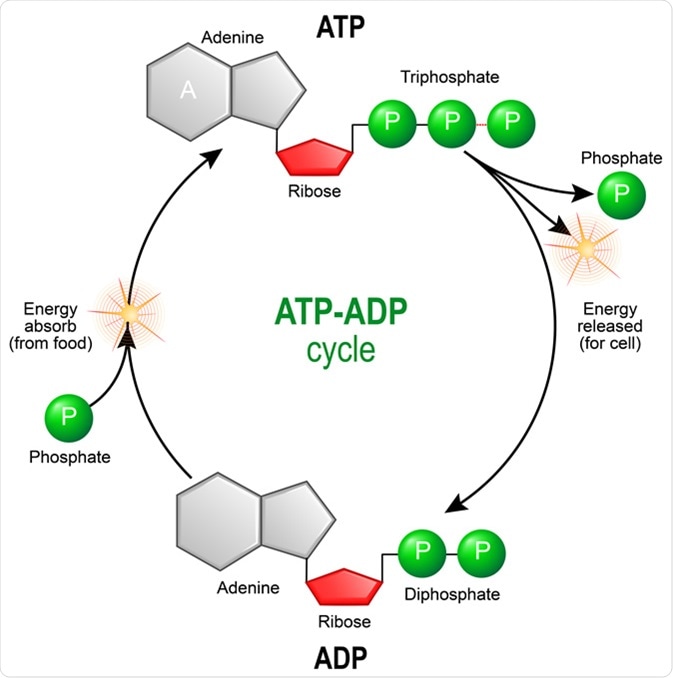
Primary metabolism is the sum of all metabolic reactions that produce essential molecules such as carbohydrates lipids amino acids and protein. Oxidative phosphorylation the process by which ATP is synthesized from ADP and inorganic phosphate Pi that takes place in mitochondrion. Define the terms metabolism metabolic pathway catabolism and anabolism.
Organic compounds also contain carbon along with other elements essential for the reproduction of living organisms. Factors affecting bioabsorption metabolism and storage of organic compounds by aquatic biota. Solution for What is Organic metabolism.
Carbon it needs to live and reproduceMicrobes use many different types of metabolic. Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical processes that enables organisms transform the chemical energy stored in molecules into energy that can be used for cellular processes. In its metabolism of food and respiration an animal consumes glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 which combines with oxygen O 2 to produce carbon dioxide CO 2 water H 2 O and energy which.
Carbon is the main factor as it has four electrons that can accommodate. Carbon is very unique in its bonding properties. Metabolism the sum of the chemical reactions that take place within each cell of a living organism and that provide energy for vital processes and for synthesizing new organic.
Understand how ATP is formed from ADP. The organic compounds proteins lipids and carbohydrates contain the majority of the carbon and nitrogen in humans whereas most of the oxygen and hydrogen is present in the. Start your trial now.
Microbial metabolism is the means by which a microbe obtains the energy and nutrients eg. First week only 499. If a test question involves identifying a compound as a carbohydrate count the atoms and see.
An organic compound is a compound that contains carbon and is found in living things. In living systems large organic molecules called macromolecules can consist of hundreds or thousands of atoms.

Metabolism Of L Tryptophan Into Serotonin And Melatonin Left And Niacin Right Transfor Organic Chemistry Books Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Education

No comments for "Explain Metabolism of Different Organic Compound"
Post a Comment